Keratoconus cross-linking
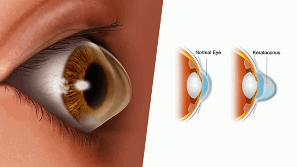
This treatment is essential to avoid or limit the risk of aggravation of the early forms with reduced visual acuity and recourse to surgical treatments: corneal transplant in particular.
The purpose of corneal collagen crosslinking is to “stiffen” a biomechanically unstable cornea.
The standard technique is, after "scraping" the corneal epithelium, by instilling riboflavin (Vitamin B2) for 30 minutes, followed by UV-A irradiation for 30 minutes.
The indications for cross-linking only concern progressive Keratoconus. It is not performed systematically in the absence of proven progression, except in children where the risk of rapid worsening is significant.
The results are consistent in the literature and report a stabilization of the disease in nearly 90% of cases. However, a number of patients may see their keratoconus continue to evolve despite treatment.